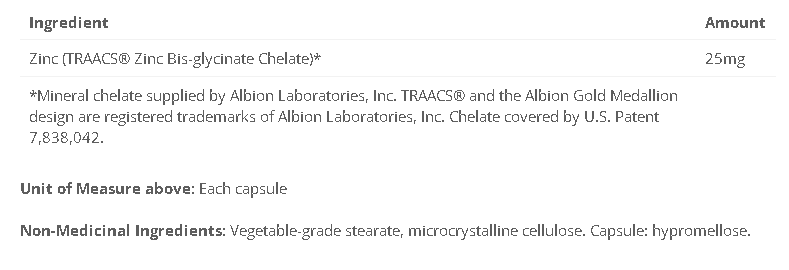


Zinc Bis Glycinate - 25mg Full Chelate
- 11.99$
0.00$- 11.99$
- Unit price
- per
Description
x- Each vegetarian capsule provides 25 mg of elemental zinc in bisglycinate chelate form for optimal absorption and tolerance
- Indicated to strengthen immunity, balance mood, improve skin health, balance various hormones and support vision
- Should also be considered in the elderly, people with digestive disorders, vegetarians, pregnant women, and people taking multiple prescription medications
People with suboptimal zinc levels typically experience symptoms of low immunity, impaired wound healing, skin conditions, and bad taste. However, these are only the most well-known signs of zinc deficiency. Zinc's role in overall health is much more complex.
Zinc's reputation as an immune-boosting mineral is well-deserved, as it is necessary for the normal development and function of natural killer cells, neutrophils, macrophages, and various cytokines. Research has shown that it can actually inhibit viral replication in the upper respiratory tract, making it particularly useful for colds and other infections.
When it comes to hormonal balance, zinc helps stabilize insulin and thus regulate blood sugar. It is also involved in thyroid health by increasing the sensitivity of triiodothyronine (T3) receptors. Finally, in men, zinc deficiency can negatively affect sperm parameters. Zinc deficiency has been shown to contribute to low testosterone levels.
Other clinical indications for zinc supplementation include eating disorders (anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa), age-related macular degeneration, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, gastric ulcers, oligospermia, and depression. Supplemental zinc has been extensively researched and shown to be beneficial in all of these conditions.
Ensuring optimal zinc levels is not only imperative in populations with the aforementioned clinical conditions, but also in special populations who, although not symptomatic, may have greater zinc needs. Populations with greater zinc needs include the elderly, patients with digestive disorders, vegetarians, pregnant women, and patients taking multiple prescription medications.
Cyto-matrix Zinc Bis-Glycinate provides 25 mg of elemental zinc in a fully chelated bis-glycinate form for optimal absorption and tolerability, with minimal risk of nausea, even in the most sensitive patients.
Produits recommandés
Produits récemment consultés
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.