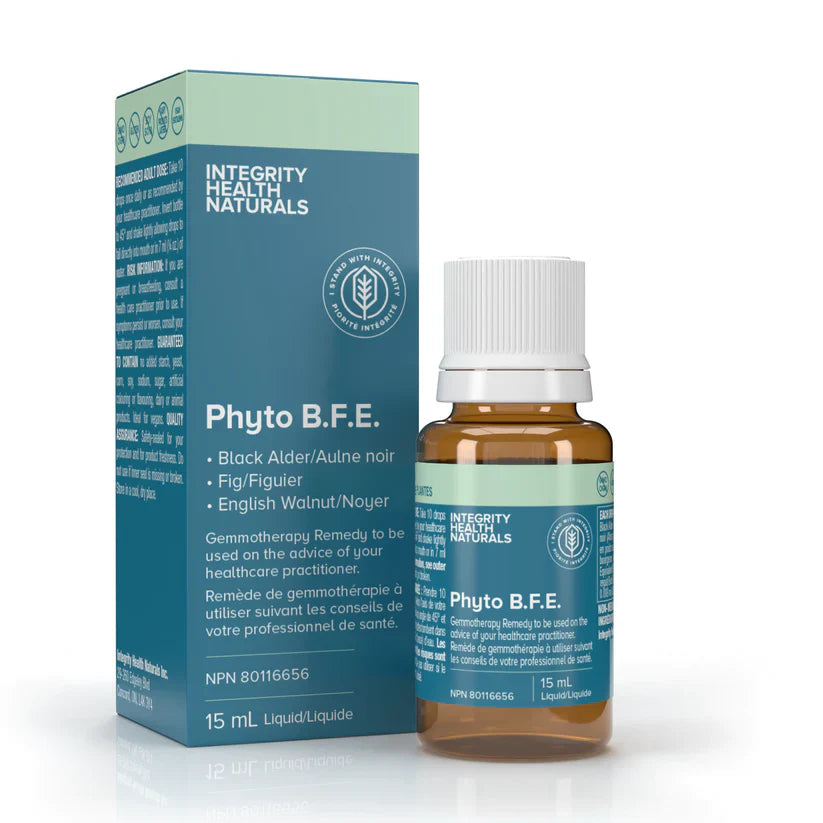
Phyto BFE
- 40.00$
0.00$- 40.00$
- Unit price
- per
Description
x- To relieve inflamed and overloaded mucous membranes
Black alder (Alnus glutinosa)
Fig tree (Ficus carica)
English walnut (Juglans regia)
Digestion plays a central role in health and disease. In Chinese medicine, dysfunction of the central burner (stomach, spleen, and gallbladder) is responsible for digestion and absorption. It is the root cause of many disorders. This idea is reflected in the Western conception of digestion and the pathologies resulting from its dysfunction.
The intestinal tract and its accompanying mucosa are responsible for communication with the external environment. Failure of this function and the resulting inflammation are the cause of many autoimmune disorders. Examples include Crohn's disease, Bechet's disease, and intestinal spondylitis.
This herbal complex promotes digestion by improving blood flow and lymphatic drainage throughout the gastrointestinal system. It thus helps combat malabsorption and pancreatic insufficiency. The remedy is also indicated as post-antibiotic therapy to help with diarrhea symptoms and promote/colonize beneficial bacteria.
Phyto BFE is used for headaches due to functional gastrointestinal disorders. Case-control studies have revealed a relationship between headaches, functional dyspepsia, and irritable bowel syndrome. There is also an inverse relationship between functional constipation and tension headaches.
Black alder is the central remedy in this complex. Its main action is to inhibit inflammation in both acute and chronic phases. Its anti-inflammatory action is said to be systematic and specific to the stomach lining.
The fig has an affinity for the digestive tract, especially the stomach. The stomach sorts everything that enters the body, including the daily "mental-emotional" events we encounter. Phrases such as "my stomach hurts" and "my guts are aching" reflect the connection between the stomach and the brain. The fig, in this combination, helps "digest" difficulties (e.g., stress) that can lead to poor digestion.
More specifically, "the fig tree manages the gastric mucosa (atrophy, hypotrophy, ulcers, gastritis), often in a context of stress." English walnut complements other remedies by providing additional anti-inflammatory protection of the digestive tract, particularly the colonic mucosa. English walnut is recommended in cases of diarrhea associated with antibiotics and to help recolonize the microbiota. Finally, English walnut also has benefits for the pancreas; in animal models, walnut appears to have hypoglycemic activity.
Produits recommandés
Produits récemment consultés
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.