
Iron SAP
- 19.99$
0.00$- 19.99$
- Unit price
- per
Description
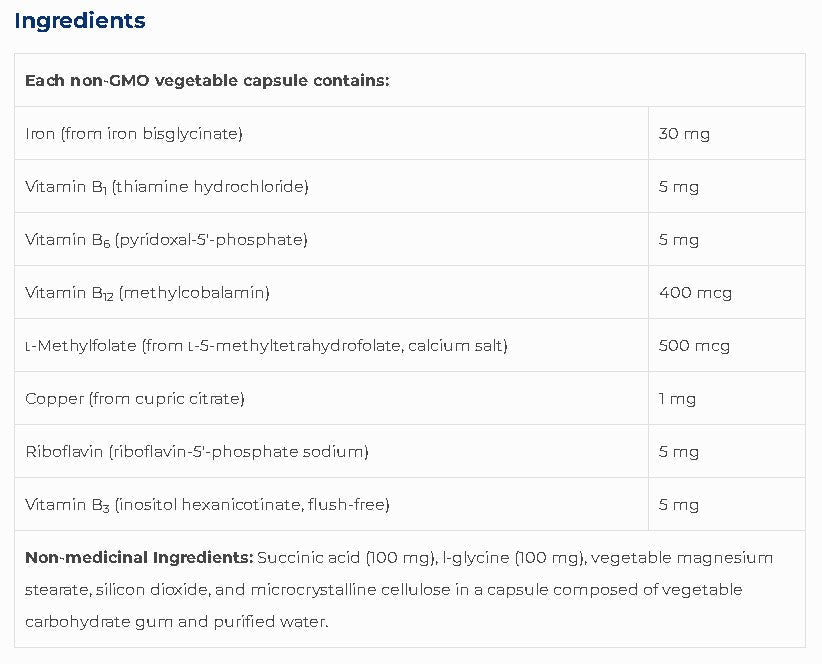
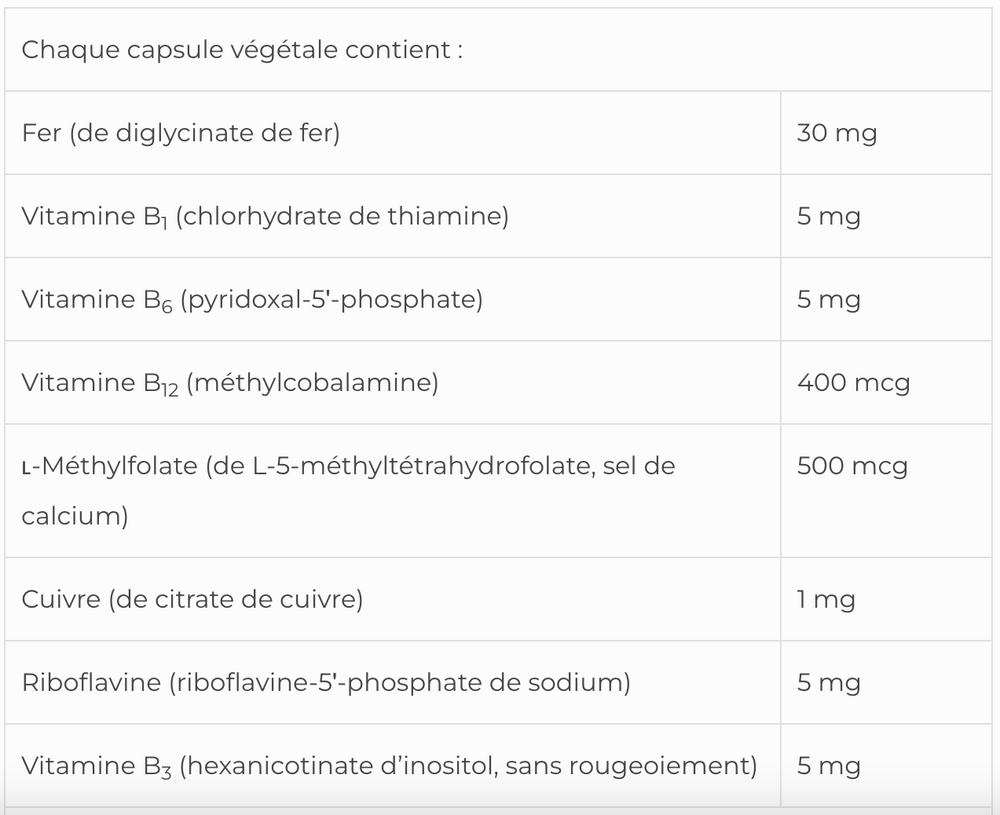
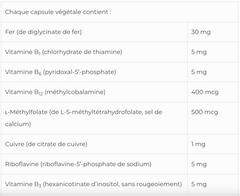
x- Iron Glycinate for Increased Bioavailability (Science Based)
Iron deficiency anemia is the most common type of anemia in North America. It can cause fatigue, weakness, headaches, and poor concentration. Women of childbearing age and pregnant women, children, undernourished workers, and the very poor are particularly vulnerable. In children, deficiency can lead to irreversible impairment of growth and cognitive development, emotional problems, and impaired immune function.
Common problems with iron supplementation include poor bioavailability, significant inhibition by dietary components (especially phytates), and gastrointestinal side effects.
Iron chelated with the amino acid glycine is more highly absorbable and elicits greater clinical efficacy than other forms, while presenting minimal digestive discomfort.
Produits recommandés
Produits récemment consultés
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.