

Cranberry SAP-UTI
- 37.99$
0.00$- 37.99$
- Unit price
- per
Please hurry! Only 3 left in stock
Subtotal:
37.99$
Description
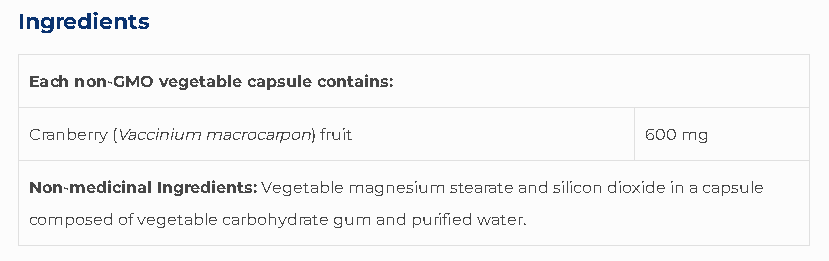
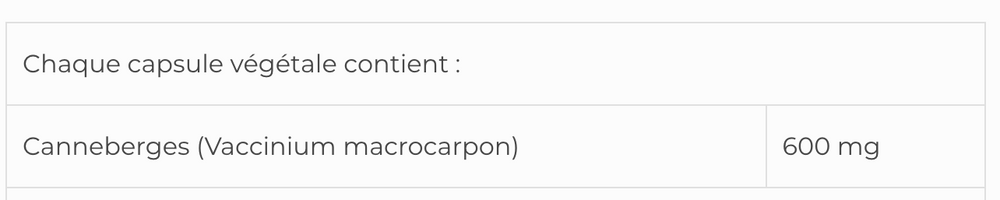
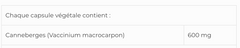
x- Cranberry Concentrate (Whole Berries) to Prevent UTIs (Science-Based)
Native to North America, cranberries have been used as a medicinal agent for centuries.
Cranberries contain proanthocyanidins, which have been shown to inhibit the fimbrial adhesion of bacteria, including Escherichia coli, to the urinary tract epithelium, thereby preventing bacterial overgrowth and infection.
It is suggested that these unique proanthocyanidin compounds, and not urine acidification, play a critical role in preventing urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Produits recommandés
Produits récemment consultés
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.