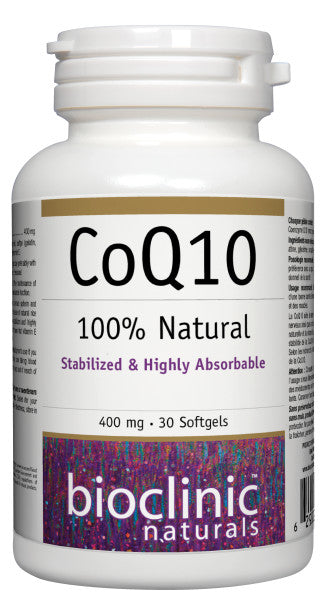



CoQ10 400 mg
- 35.99$
0.00$- 35.99$
- Unit price
- per
Description
x- Identical to the form produced by the human body for high bioavailability
- Improves many health problems, including cardiovascular disease, cell breakdown, and oxidative stress.
- The higher dosage of 400 mg reduces the need to take multiple pills throughout the day and follows evolving research.
- Free from contamination by unwanted residues or microorganisms, including bacteria or yeasts
- In a base of natural rice bran oil and vitamin E to ensure a stabilized and highly absorbable form of CoQ10.
The majority of CoQ10's clinical uses are based on its role as an antioxidant and its role in mitochondrial bioenergetics. It is a coenzyme for many reactions involved in cellular respiration and is required for the efficient formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cellular currency that fuels the majority of enzymatic reactions. It inhibits the peroxidation of cell membrane lipids as well as circulating lipoproteins.3,4 CoQ10 supports cardiac tissue by improving endothelial function and having a direct anti-atherogenic effect, which results in lowered blood pressure and improved ventricular contractility.
High doses of CoQ10, up to 2400 mg per day, have been used primarily for neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease and Huntington's disease, although high doses have also been used in patients with severe cardiovascular disease or advanced breast cancer. Clinical trials have shown benefits for a wide range of cardiovascular conditions, including congestive heart failure, hypertension, and prevention of myocardial infarction. It has also shown clinical benefits for several other conditions, including migraine, periodontal disease, gingivitis, male infertility, and statin-induced myopathy.
Produits recommandés
Produits récemment consultés
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.