
AC Capsules
- 54.99$
0.00$- 54.99$
- Unit price
- per
Description
x- Promotes good glucose metabolism
- Source of amino acids involved in muscle protein synthesis
- Helps maintain good mood balance
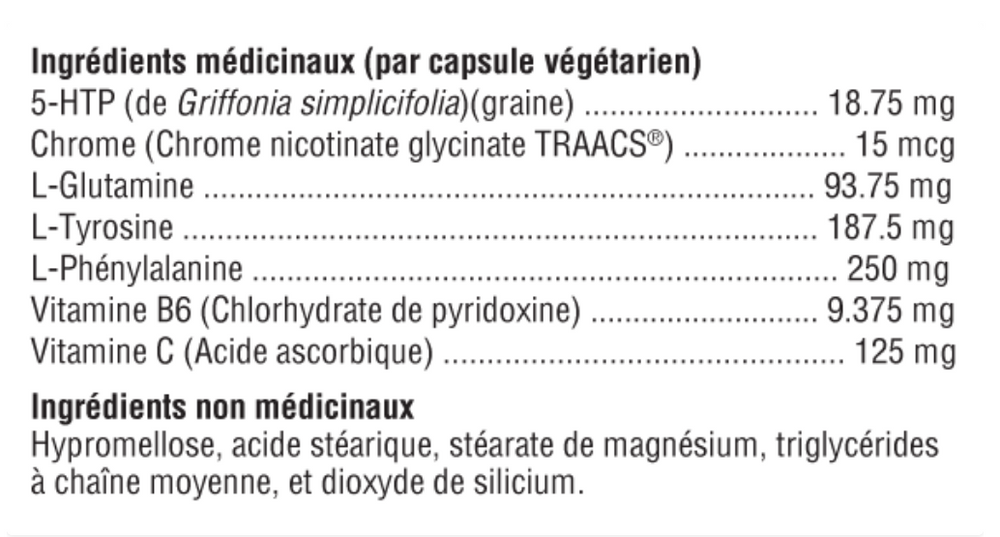
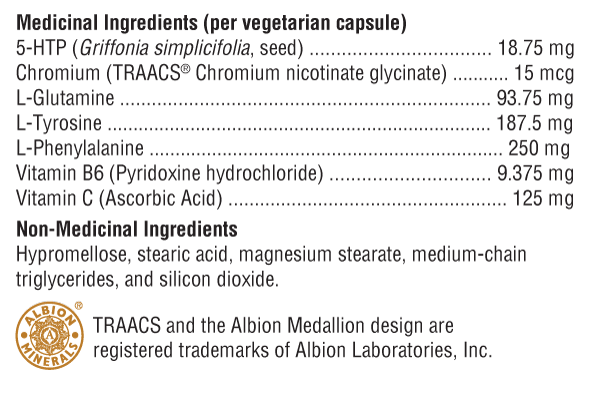
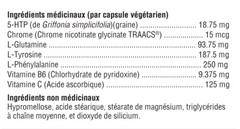
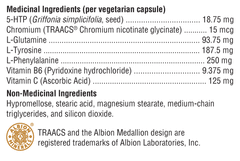
5-Hydroxytryptophan ("5-HTP") is a naturally occurring amino acid precursor of serotonin. Numerous studies during the 1990s, including randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled studies, confirmed the safety and efficacy of 5-HTP in reducing appetite and food intake in healthy, obese diabetic individuals with non-insulin-dependent leptin secretion. Vitamins B6 and C are important cofactors in the 5-HTP to serotonin pathway. Among the many serotonin receptors thus identified, 5HT2C receptors are suspected of controlling food intake. Mice lacking this receptor exhibit increased food consumption and become obese.
DL-Phenylalanine (DLPA) is a combination of the d- and l-forms of this essential amino acid. Phenylalanine suppresses appetite by regulating the release of cholecystokinin, which in turn signals satiety in the brain. D-Phenylalanine increases endorphins, while L-Phenylalanine is an amphetamine-like stimulant compound. DLPA has been shown to improve mood, curb appetite, and reduce pain.
L-Tyrosine, an essential amino acid, is necessary for conversion to the stress-relieving catecholamine neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. It is also a precursor to thyroxine. Doctors use tyrosine as a mood elevator, to increase alertness after sleep deprivation, and as an appetite suppressant; although support for the latter appears anecdotal.
L-Glutamine, known for its intestinal and immune support, has also been adopted to reduce carbohydrate cravings and aid alcohol withdrawal, although the mechanism of action for these benefits is not known.
Chromium, as chromium picolinate, is widely used to optimize insulin function, thereby preventing blood sugar fluctuations that can be responsible for carbohydrate cravings. In fact, the mineral in its present form was shown to reduce carbohydrate cravings in a double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
Produits recommandés
Produits récemment consultés
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.